What is a Stormwater BMP?
Stormwater Best Management Practices (BMPs) are a practice or a combination of practices that provide a level of treatment and/or storage to improve the water quality of watersheds. Likewise, BMPs are an effective and practicable means of preventing or reducing the amount of non-source pollution to a level compatible with water quality goals.
Stormwater BMP Design & Installation
Please refer to the Maryland Stormwater Design Manual, Volumes I and II for minimum requirements and procedures for maintaining BMPs. This document serves as the official guide for stormwater management principles, methods, and practices in the State of Maryland.
Do you want to manage stormwater more efficiently on your property, but you aren't sure where to start? The Anne Arundel County Watershed Stewards Academy, an environmental capacity-building nonprofit based in Anne Arundel County, offers a wealth of resources to help you get the job done. Visit their website and/or schedule a free Residential Site Assessment with a certified Master Watershed Steward to get started!
Residential and commercial property owners may be eligible to receive a credit towards their County real property taxes for the recent installation of qualified stormwater management practices. Please see the Stormwater Management Property Tax Credit Program webpage to learn more.
Stormwater BMP Maintenance
These practices can be found Countywide in a variety of applications such as a wet pond in a residential area or a rain garden at a private residence. As such, all BMPs require periodic maintenance. The inspection and maintenance interval is BMP-specific. Maintenance is typically divided into two types: routine and non-routine. Effective BMP performance requires regular and effective maintenance.
BMP maintenance is the responsibility of the entity owning the BMP. Publicly owned BMPs are maintained by the County while privately owned BMPs typically are maintained by the property owner, homeowner’s association, or property manager. In some cases, privately owned BMPs may be maintained by the County under a written agreement with the owner.
Is there a stormwater practice in your community that the County is responsible for maintaining?
To report a problem with a County-maintained BMP, please call the Bureau of Watershed Protection and Restorations Infrastructure Management Division at (410) 222-4240 between the hours of 7:30 a.m. and 4:30 p.m., Monday through Friday. Your request will be investigated within one week, and you will be notified of a schedule for the resolution of the problem.
You may also submit requests online via SeeClickFix.
Are you responsible for maintaining a stormwater BMP on your property?
Below is a selection of typical BMPs found in the region and suggested maintenance actions to keep your BMP functional to ensure water quality is protected.
Eligible property owners in Anne Arundel County have the opportunity to reduce their Watershed Protection and Restoration Fee (WPRF) assessments by up to 50% for proactive and sustainable uses of stormwater runoff controls. Please see the WPRF Credit Program webpage to learn more.
Please note: The below maintenance guidance is intended to provide property owners with routine maintenance suggestions of BMPs they are responsible for maintaining and is not intended to replace professional maintenance and inspection of a facility. Be sure to follow all manufacturer's recommendations where applicable.
A buried dry well is a small underground pit filled with stone that collects rainwater from roof gutters and allows it to absorb into the surrounding soil. Underground piping connects the dry well to the roof downspout. Dry wells are common on residential lots, where there can be three or more dry wells on one lot. Since most are buried and covered with grass, dry wells can be identified by an observation well cap that is typically around 20 feet from the house.
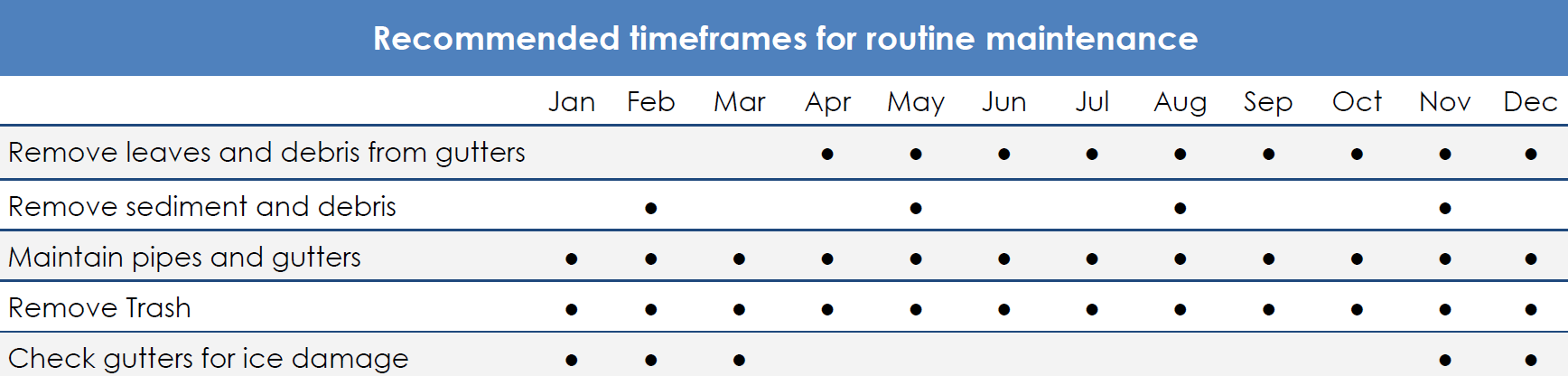
Swales are one of the most commonly used stormwater practices. For many years, they have been used along highways, parking lots, along residential streets, and in between homes to convey water. Swales are designed to slow and infiltrate stormwater runoff.
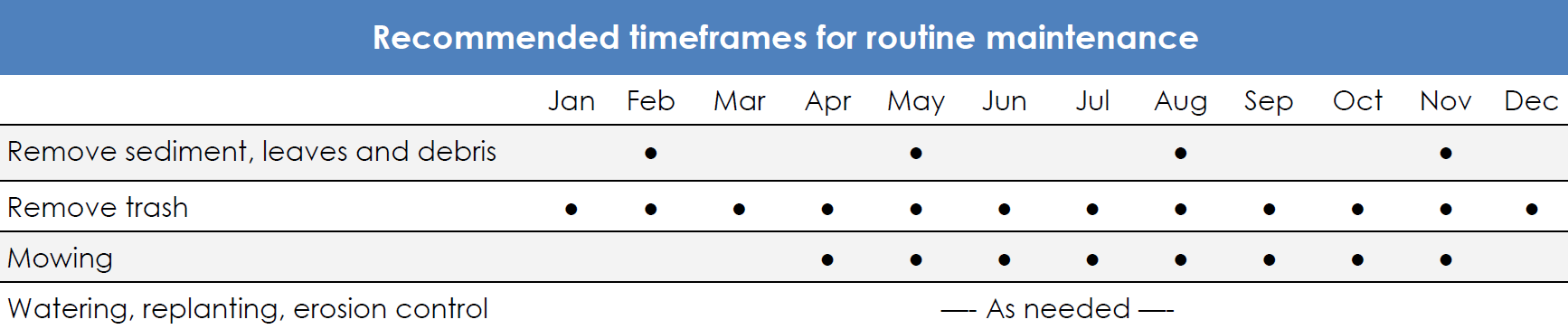
An infiltration area is a small trench filled with stone that collects rainwater from paved surfaces such as driveways and allows it to absorb into the surrounding soil. An infiltration area receives rainwater from surface runoff and are common on residential lots, where they are typically located next to driveways and around 20 feet from a building. Their location can be identified by the stone at the surface.
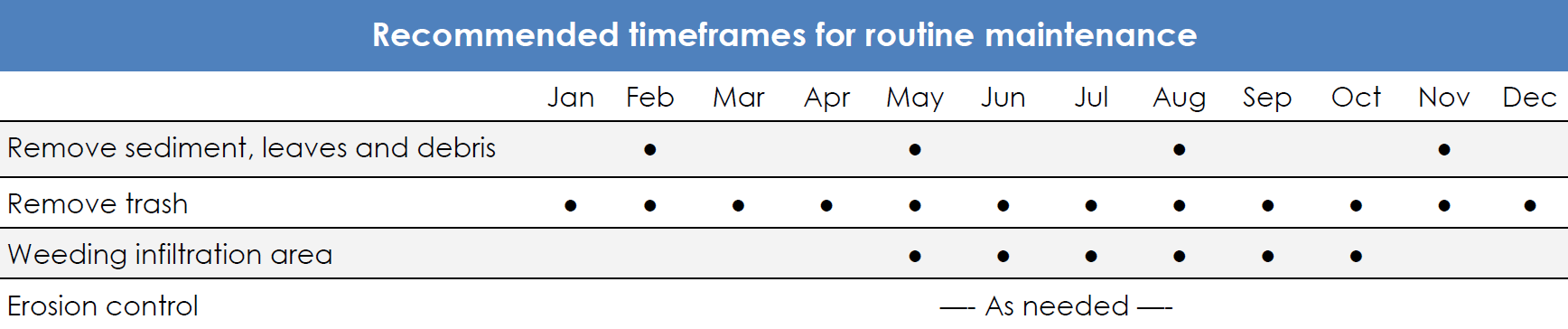
Pervious pavement consists of a block or porous pavement layer that is underlain by gravel and sand layers in most cases. This BMP is intended to be used in parking lots and in low traffic areas to accommodate vehicles while facilitating stormwater infiltration near its source.
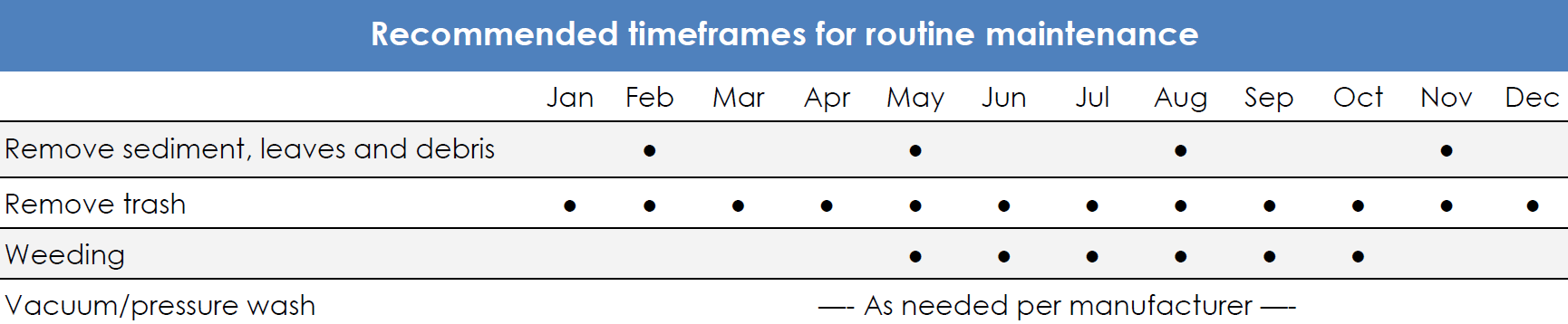
Rain gardens are landscape features that store and treat stormwater runoff. Surface runoff is directed into shallow, vegetated depressions with underlying layers of soil, sand, and gravel. These areas are designed to mimic natural ecosystems where pollutant removal occurs through soil infiltration and plant uptake.
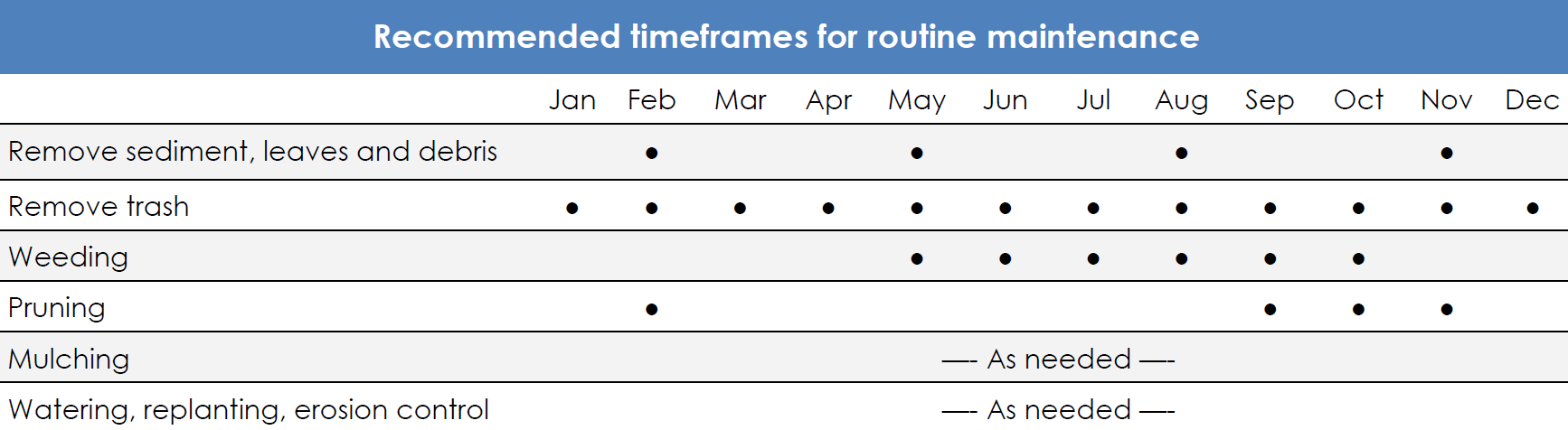
Rain Garden/Bioretention Maintenance Sheet
Article - "Utilizing Rainwater and Gravity: A Guide to Rain Gardens" by Andy Darnley
A structural BMP used to capture and treat a volume of stormwater runoff. This BMP is an excavated basin containing a sand filter bed, with an under drain system. Runoff collects in the basin and gradually infiltrates into the sand bed. The under drain then dewaters the sand bed and flows are conveyed to a nearby swale or storm drainage. An outfall is used to drain higher volumes of flow.
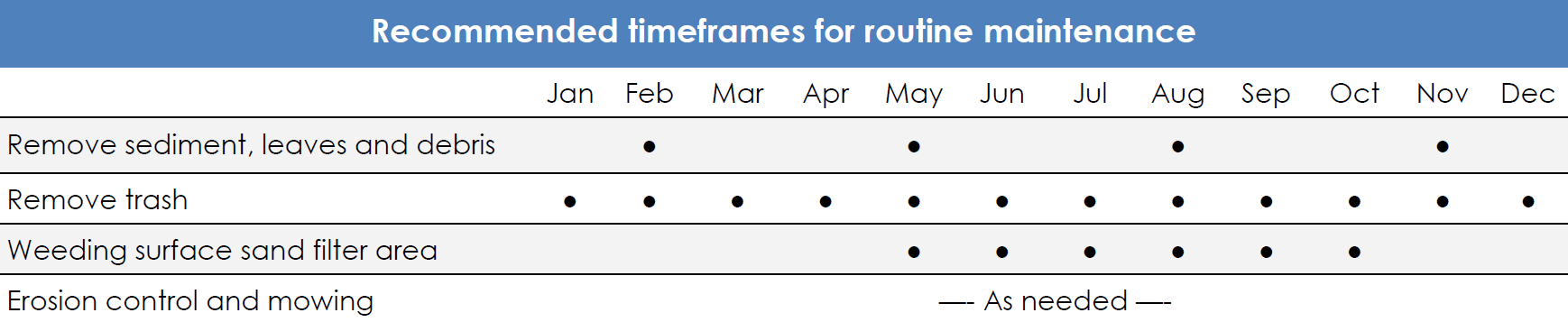
SPSCs are open-channel conveyance structures that convert, through attenuation ponds and a sand seepage filter, surface storm flow to shallow groundwater flow. These systems safely convey, attenuate, and treat the quality of storm flow. These structures utilize a series of constructed shallow aquatic pools, riffle grade control, native vegetation, and an underlying sand/woodchip mix filter bed media.
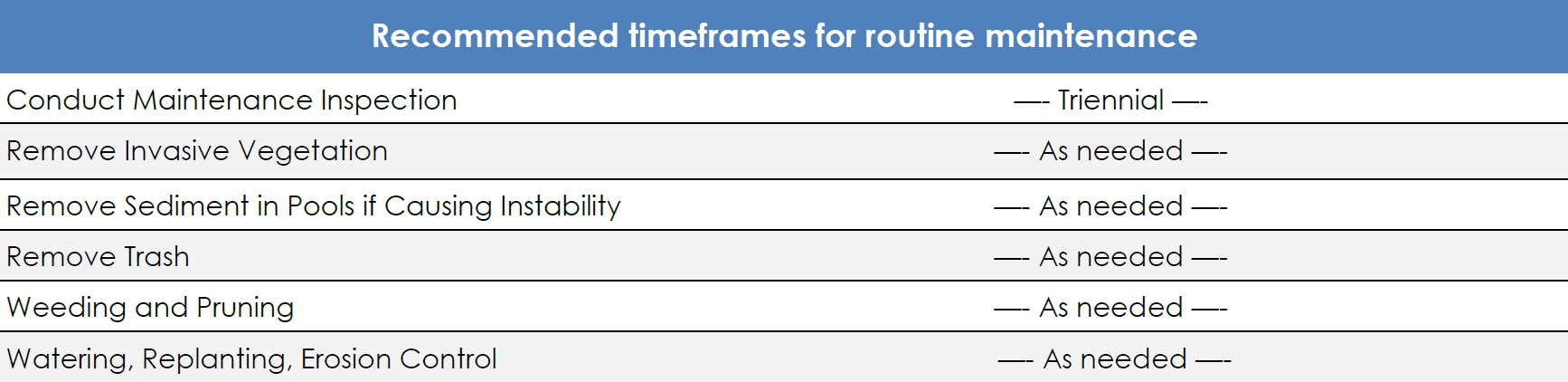
A dry pond is a SWM facility that is designed to hold stormwater runoff, then release the runoff over a period of time. The purpose of a dry pond is to allow time for pollutants and sediment to settle out of water, and to manage the volume of stormwater runoff in order to prevent floods. A dry pond generally appears to be a grass basin. It is not designed have a permanent pool of water, and therefore should not have standing water during dry weather conditions.
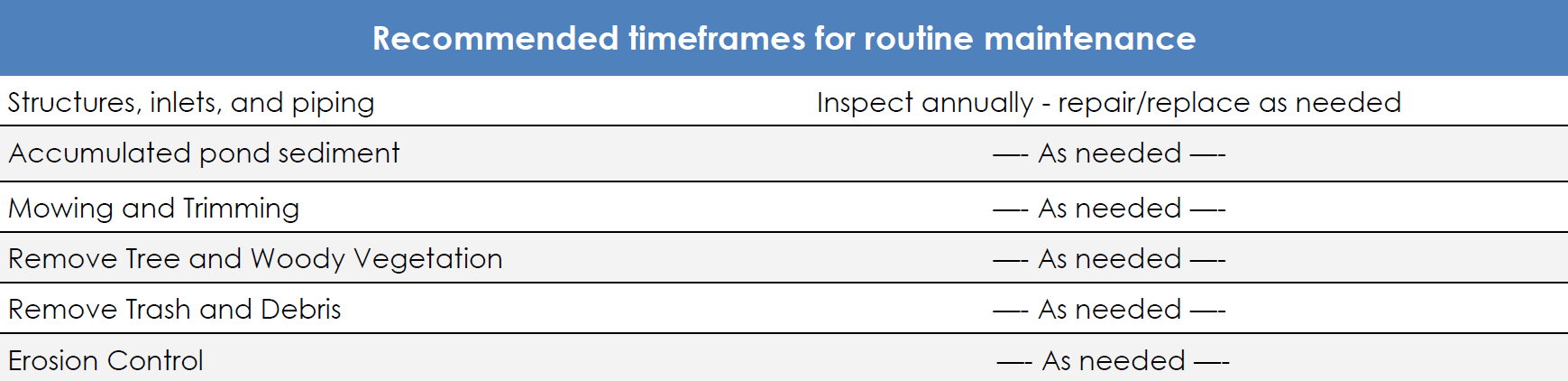
Wet ponds, also known as retention basins, are used to address the stormwater quantity and quality impacts of land development. This type of stormwater facility has an elevated outlet structure that creates a permanent pool where stormwater runoff is detained and attenuated. Wet ponds can be designed as multi-stage, multi-function systems; extended detention in the permanent pool provides pollutant treatment for runoff from the Water Quality Design Storm through sedimentation and biological processing; detention and attenuation are also provided for larger storm event through the higher elevation outlets.
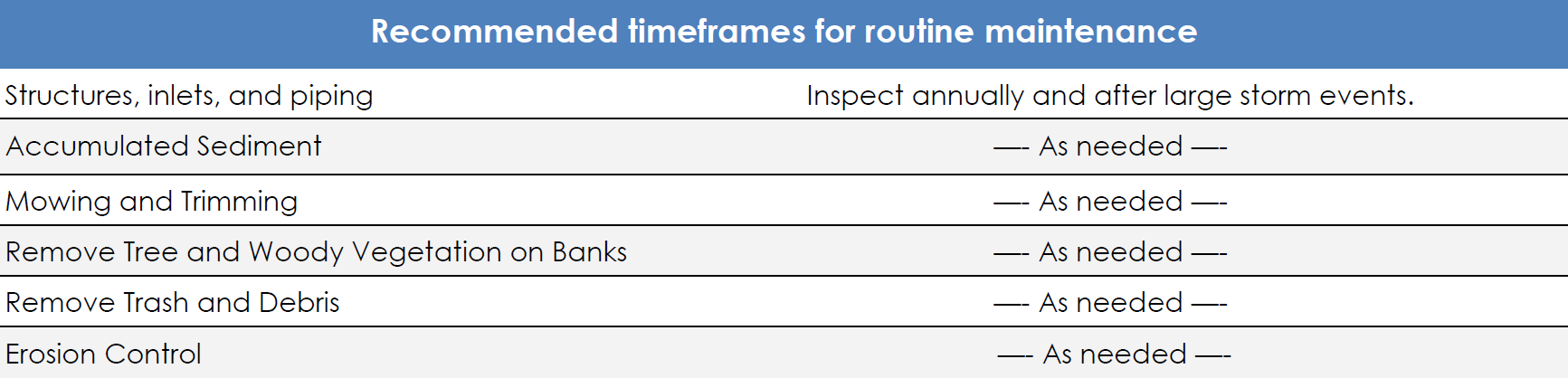
Constructed wetlands are stormwater management systems designed to maximize the removal of pollutants from stormwater runoff. Constructed wetlands are typically shallow marsh systems planted with emergent vegetation. Flow is directed through an engineered, open marsh system where pollutants are removed through settling and vegetative uptake/filtration.Constructed wetlands can be designed as either an online or offline facilities. They can also be used effectively in series with other flow/sediment reducing BMPs that reduce the sediment load and equalize incoming flows. Constructed wetlands are a good option for retrofitting existing dry ponds.
Contact Us
For questions or to inquire about a site visit, please contact our Education and Outreach Coordinator, Sally Albright, via email at pwalbr00@aacounty.org or by phone at (410) 222-0136.

